The software industry has a reputation butchering great ideas into things that we call the same but in the end are being mis-used completely compared to the initial concepts. Take “Agile”. Everyone is working sprints or using Kanban but a lot of companies are far from actual the actual agile concepts. People use Jira so they are Agile. Same goes for DevOps where a lot of traditional operations teams were rebranded to ops so now they do devops 🤷 , Microservices: just cut your monolith into pieces so you get a large distributed monolith which isn’t better than the monolith 🤷.
The problem is often that vendors try to help out with certain problems and then companies think they can just buy Agile by using Jira, You can buy DevOps by using Azure DevOps, Github or Gitlab. A lot of software vendors enable you do do these things better but it’s far more than just these tools. It’s also they way you work, communicate and your internal operating model.
One of the latest hypes is “Platform Engineering”. The idea behind it is pretty good (I’ll come back to that in a moment) but the term is already broken before most people actually know what it is because vendors who create “platform engineering tools” butcher the term Platform Engineering. Slogans as “DevOps is dead, use Platform Engineering” totally miss the point. It’s NOT another rebrand of your operations department after rebranding it to DevOps or SRE. In my humble opinion the only thing that matters is setting up an organizational structure that works best FOR YOUR COMPANY (which is different from all other companies so stop copy pasting things from other companies without thinking what works for you).
TLDR: I see DevOps as a way of working that you could implement in several ways. Platform Engineering and SRE are implementations of this.

DevOps, SRE, Platform Engineering?
All 3 terms are used in so many different ways at companies. Are they really different? Are they different implementations of the same thing or do they complement eachother?
DevOps
DevOps, a term used for quite a while now in our industry. There are a lot of different opinions about what DevOps is. To me it is much more than just putting some devs and operations people together. It’s about creating autonomous teams who focus on delivering business value in a better & faster way. It’s a combination of People, processes and tools all working together for the goal of delivering a better product faster.
Autonomy in this is key. Giving a lot of freedom to teams to live the mantra: “You build it, you run it.” This means teams should have the capabilities and responsibilty to make decisions themselves on almost everything. The software they build, the cloud infrastructure they run on, the network that connects their components, the database that stores their data..
These autonomous teams have proven to be highly effective but they also come with a burder. Engineers now need to know more from a lot of things instead of only focus on the code they write. SRE and Platform engineering are forms that can help release this burden.
SRE
SRE, (Site Reliability Engineering) Invented by Google is a way to add extra reliability to software products by having engineering teams who focus mainly on Reliability. This does not mean that they fix issues for DevOps teams but they are truely engineers who have a lot of expertise in creating reliable software products and can help the DevOps team in improving the way their product works from a reliability perspective.
At Google DevOps teams need to earn the addition of a SRE team for their product by proving their product is delivering enough business value.
In this definition of SRE, SRE should not be compared to DevOps. It is just a way of implementing DevOps for large organizations releasing some of the burden of creating high reliable software products when products need to scale to the immense scale of a company like Google.
Platform Engineering
Platform Engineering teams, the newest hype in creating high performing software organizations should be a similar addition to implementing DevOps if you ask me. The core principle is also releasing the burden of the DevOps teams by creating standardized software platforms that autonomous DevOps teams can use. This can be all kinds of products like container hosting platforms, firewall & network controlls, API Management, Cloud infrastructure platforms, DevOps tooling platforms, you name it.
What I don’t like about the current platform engineering hype is that there is a really large push on platform engineering products who also mainly focus on kubernetes. Platform engineering teams should NOT be about pushing a platform to autonomous DevOps teams but should rather be ran as an internal product team who’s product can be used by DevOps teams if they think this would be a great fit for them.
If DevOps teams would decide not to use the platform that should be just fine! The platform engineering team should create a product that actually delivers value to the DevOps teams and not burden them in such a way that might hinder the DevOps team to deliver business value.
Who needs Platform Engineering?
In current times where we build modern software I think there is a great place for platform engineering. Autonomous DevOps teams have to focus on so many things that require extra expertise and knowledge that it makes it harder and harder to execute. In these cases Platform engineering can be the answer to make the DevOps teams working on a certain value stream focus more on the actual value tream and use services provided by the platform engineering team.
Platform engineering teams can also focus a lot more in getting to know all the details and focus on tuning underlying infrastructure or software where a DevOps team focussing on a business value stream does not have time for. Key thing here is though that they should never become a bottleneck for these DevOps teams.
Some examples I’ve seen & helped build at companies:
Cloud Platforms
Self service cloud platforms where teams can get their own “landing zone” to create cloud infrastructure and deploy their applications in.
Container hosting platforms
Everyone uses Kubernetes nowadays.. Kubernetes does have many cool features but lets face it. It’s also really hard to maintain & make secure even if you use one of the managed offerings of the major cloud providers. Having this be managed by teams who also have to focus on business value will cost them a lot of effort they could spend on delivering business value.
Api management platforms
As a company you want to be sure that integrations with customers or 3rd parties are made in such a way that everything is consistent. A centralized API management platform helps in creating such a place that is the single entrace for your integration partners where DevOps teams can publish their APIs.
Firewall and network platforms
Creating a safe boundary around your network is often complex to make secure but still convinient for DevOps teams to use in an autonomous way. Creating a self service solution here can really help in making it possible for DevOps teams to expose their applications to the outside world without waiting for approvals or the networking team executing the changes for the DevOps team.
DevOps tooling platforms
Teams need tools to build their software. In large organizations the teams that maintain these tools can become a bottleneck for other teams that actually want to use these tools. Self service enablement for onboarding, settings, offboarding can help reduce the wait for DevOps teams to get things done and can help in getting teams working on the golden path that helps in compliance & security.
IAM Platforms
Within a company you want all applications to be able use the same identity for your users so they can use single sign on throughout the different applications. If you make it possible for teams to onboard their own apps to this identity platform.
If you see some other examples of platform engineering teams let me know in the comments!
Conclusion
Platform engineering can be a great way to empower your DevOps teams to be more productive. Focus on making golden path implementations easier through self service but leave the responsibility on making choices at the DevOps teams. Internal platforms that are optional are the best way to go. If a team decides not to use it that’s fine. It does mean they have to own things like compliance & security themselves but if that is worth it for them it’s OK. Run your platform teams as internal products. have a product vision and treat your other internal teams as actual customers. A Platform engineering team should in the end just be another DevOps team that is responsible to build & run their platform as a product in the same way DevOps teams run their software as a product.
I think the book “Team Topologies” does a great job in describing relations between teams. DevOps teams should act as “Stream aligned teams”. Focussing on a certain business capability. Platform teams should not act as a enabling team but rather just be a “platform team” that as I wrote earlier provides a platform that teams can choose to use. An SRE team could act in the form of “Enabling team” working together with both the Platform engineering teams and the DevOps teams.
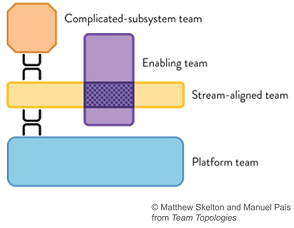
My final conclusion is that all these things are ideas and concepts that should help you deliver software & value to your end customers faster and with better quality. Therefore I see all of this as a form of DevOps instead of competing visions.
I started this blog a week ago and it’s actually my 3rd blog I created. I created my first blog around 2010 as self hosted wordpress website. Then when doing more Azure stuff I wanted to start of with a clean cheat again and created a new blog in 2016 using Wordpress again but then hosted on Azure https://mobilefirstcloudfirst.net. This worked but I was never happy with it. The last 2 years I didn’t blog at all so when I started with my new years resolution of blogging again I decided I needed a new blog, new domain name and something that used markdown for editing.
Choosing Hugo
I chose Hugo after looking into some of the common blogging platforms that are based on static site generators such as Jekyll and Hugo. After browsing through some of the themes and did some comparison I decided to try out Hugo since it looked more popular and just wanted to see how ard it was.

A couple of hours later the website was up and running on my machine and I was already tweaking away at some UI improvements.. Point proven lets see what I needed to do.
My blog using Hugo hosted on Github Pages, what is in the box?
I wanted to create a blog website that was based on markdown files that i could store in git. I already had some experience with GitHub Pages so I though lets see how hard that is. After a couple of hours I had the followng up and running:
- Hugo CMS
- Finding a theme
- Algolia Search
- GitHub Pages for hosting
- Github discussions for comments using Giscuss
- Automatically deploy using Github Pages
Hugo CMS
The Hugo CMS was quite easy. I just followed the tutorial on the Hugo website to create a new empty website. It took me a couple of minutes.
Adding a Theme
Hugo has a list of themes on it’s website. The Clean White Hugo Theme looked quited good so I gave that a go. What I looked for in a theme was a nice clean interface and options for comments + search. This team had it all so I just installed it as a git submodule and when I ran the hugo serve command it was working from the get go
mkdir themes
git submodule add https://github.com/zhaohuabing/hugo-theme-cleanwhite.git themes/hugo-theme-cleanwhite
After my initial playing around with setting up the website I wanted to customize some things so what i did was that I actually forked the github repo and made the changes on my fork. All my changes are open source and can be found on this repo
Changes that I made are:
- Showing blog preview / full posts in the homepage instead of the really small summaries.
- Added headers to the blog preview using images
- Added an option to show banners on the sidebar.
- Some small css tweaks
- Added full posts to the RSS Feed instead of the summary
- Fixed some issues in the algolia search json that was being generated
All these changes were quite simple without me knowing anything about Hugo, themes or GO templating.
Algolia Search
Hugo does not have support for search out of the box by itself. Luckely the theme I chose had this covered and supported search by a free 3rd party service. The only thing that was needed was creating an account and set up the API key and create an index.

Algolia works with sending json files to the index. The json files are generated during compilation of the Hugo website and this json can then be uploaded on the website of Algolia for a first test. This manual labor is not something I would prefer so I automated this in the next step where I also deploy everything to Github Pages.
Deploying every commit to Github Pages and host it on my custom domain

I’m a developer so I wanted a fully automated workflow. My content is stored in a git repo on Github and I wanted that every commit I made to main would be automatically deployed to the website.
GitHub offers this flow with no effort for Jekyll but for HUGO some small additions needed to be done. Before we create our workflow we need to add a specific file to our repo called CNAME so github pages links this page to our custom domain.
CNAME File
When you change the domain name for your website hosted using GitHub pages Github automatically creates a commit with a CNAME file in it. This file is used by GitHub to know which domain name is used for the website. Since my workflow was pushing all contents of the ./public folder GitHub was actually removing this file every time after the Hugo workflow ran. Manually adding the CNAME file to the static folder helped solve this issue.
My CNAME file content:
fullcycledeveloper.com
Now that everything is ready we can create our workflow file. My file looks like this, The steps are quite self explanatory but I’ve added some comments below each action to explain what I’m doing.
name: github pages # Name of the workflow
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
defaults:
run:
working-directory: blog
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
with:
submodules: true # Fetch Hugo themes (true OR recursive)
fetch-depth: 0 # Fetch all history for .GitInfo and .Lastmod
- name: Setup Hugo
uses: peaceiris/actions-hugo@v2
with:
hugo-version: 'latest'
# Downloads & installs HUGO cli
- name: Build
run: hugo --minify
# Do a HUGO build of your markdown files to generate a stetic website that is stored in the `./public` folder
- name: Deploy
uses: peaceiris/actions-gh-pages@v3
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main'
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
publish_dir: ./blog/public
# takes the public folder and pushes the changes to a new branch called gh-pages
- uses: wangchucheng/algolia-uploader@master
with:
app_id: 9AWS4CUHVW
admin_key: ${{ secrets.ALGOLIA_ADMIN_KEY }}
index_name: fullcycledeveloper-blog
index_file_path: ./blog/public/algolia.json
# Uploads the algolia json file to the index on algolia website
After each commit the generated website is pushed to the gh-pages branch. From here we can enable Github Pages in the Settings menu of the repository. Point it to the right branch and connect the domain name that you specified in the CNAME file. You’ll have to do some DNS settings to make sure you are the actual owner of that domain and voila your website is ready to go!
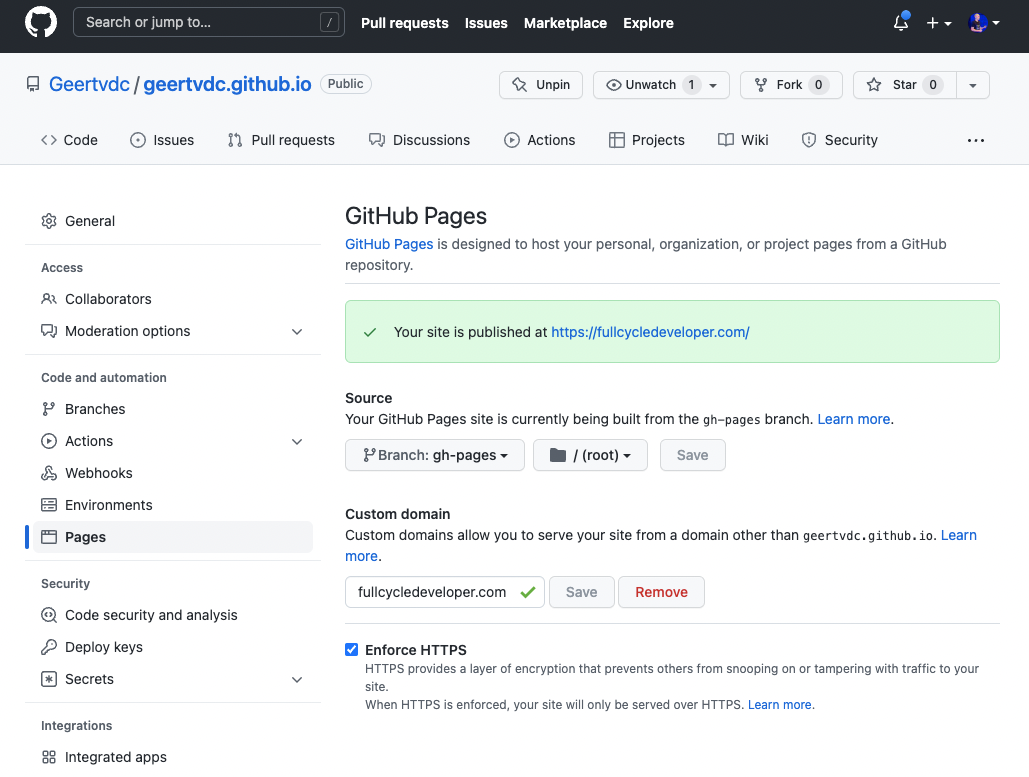
Adding comments to the posts using Giscuss (based on Github Discussions)
A static website by default is just static.. That is ok for most scenarios but for a blog I wanted to add comments to the posts. I used Giscuss to do that. The Hugo Theme I used (Clean White Hugo Theme ) has built in support for multiple comment systems. Since my main target audience is developers I chose Giscuss as the comment system.
The only thing i needed to do is set the properties to the right Github Discussions space in my configuration .toml file.
[params.giscus]
data_repo="geertvdc/geertvdc.github.io"
data_repo_id="<REPO_ID>"
data_category="blog-comments"
data_category_id="<CATEGORY_ID>"
data_mapping="blog"
data_reactions_enabled="1"
data_emit_metadata="0"
data_theme="light"
data_lang="en"
crossorigin="anonymous"
After doing that it just works! I didn’t have to sign up for any new platform since my code is already on Github and now everything is in the same place.
Hopefully this helps people set up a simple blog website as well. I’m really happy in how it turned out and it really was a breeze to set it up.
Happy Blogging!
Geert van der Cruijsen


